The Object Detector task lets you detect the presence and location of multiple classes of objects. For example, an Object Detector can locate dogs within an image. These instructions show you how to use the Object Detector task in iOS. The code sample described in these instructions is available on GitHub.
You can see this task in action by viewing this Web demo. For more information about the capabilities, models, and configuration options of this task, see the Overview.
Code example
The MediaPipe Tasks example code is a basic implementation of an Object Detector app for iOS. The example uses the camera on a physical iOS device to continuously detect objects, and can also use images and videos from the device gallery to statically detect objects.
You can use the app as a starting point for your own iOS app, or refer to it when modifying an existing app. The Object Detector example code is hosted on GitHub.
Download the code
The following instructions show you how to create a local copy of the example code using the git command line tool.
To download the example code:
Clone the git repository using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/google-ai-edge/mediapipe-samplesOptionally, configure your git instance to use sparse checkout, so you have only the files for the Object Detector example app:
cd mediapipe-samples git sparse-checkout init --cone git sparse-checkout set examples/object_detection/ios/
After creating a local version of the example code, you can install the MediaPipe task library, open the project using Xcode and run the app. For instructions, see the Setup Guide for iOS.
Key components
The following files contain the crucial code for the Object Detector example application:
- ObjectDetectorService.swift: Initializes the detector, handles the model selection and runs inference on the input data.
- CameraViewController.swift: Implements the UI for the live camera feed input mode and visualizes the detection results.
- MediaLibraryViewController.swift: Implements the UI for the still image and video file input mode and visualizes the detection results.
Setup
This section describes key steps for setting up your development environment and code projects to use Object Detector. For general information on setting up your development environment for using MediaPipe tasks, including platform version requirements, see the Setup guide for iOS.
Dependencies
Object Detector uses the MediaPipeTasksVision library, which must be installed
using CocoaPods. The library is compatible with both Swift and Objective-C apps
and does not require any additional language-specific setup.
For instructions to install CocoaPods on macOS, refer to the CocoaPods
installation guide.
For instructions on how to create a Podfile with the necessary pods for your
app, refer to Using
CocoaPods.
Add the MediaPipeTasksVision pod in the Podfile using the following code:
target 'MyObjectDetectorApp' do
use_frameworks!
pod 'MediaPipeTasksVision'
end
If your app includes unit test targets, refer to the Set Up Guide for
iOS for additional information on setting up
your Podfile.
Model
The MediaPipe Object Detector task requires a trained model that is compatible with this task. For more information about the available trained models for Object Detector, see the task overview Models section.
Select and download a model, and add it to your project directory using Xcode. For instructions on how to add files to your Xcode project, refer to Managing files and folders in your Xcode project.
Use the BaseOptions.modelAssetPath property to specify the path to the model
in your app bundle. For a code example, see the next section.
Create the task
You can create the Object Detector task by calling one of its initializers. The
ObjectDetector(options:) initializer sets values for configuration options
including running mode, display names locale, max number of results, confidence
threshold, category allowlist and denylist.
If you don't need an Object Detector initialized with customized configuration
options, you can use the ObjectDetector(modelPath:) initializer to create an
Object Detector with the default options. For more information about configuration
options, see Configuration Overview.
The Object Detector task supports 3 input data types: still images, video files
and live video streams. By default, ObjectDetector(modelPath:) initializes a
task for still images. If you want your task to be initialized to process video
files or live video streams, use ObjectDetector(options:) to specify the video
or livestream running mode. The livestream mode also requires the additional
objectDetectorLiveStreamDelegate configuration option, which enables the
Object Detector to deliver detection results to the delegate asynchronously.
Choose the tab corresponding to your running mode to see how to create the task and run inference.
Swift
Image
import MediaPipeTasksVision let modelPath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "model", ofType: "tflite") let options = ObjectDetectorOptions() options.baseOptions.modelAssetPath = modelPath options.runningMode = .image options.maxResults = 5 let objectDetector = try ObjectDetector(options: options)
Video
import MediaPipeTasksVision let modelPath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "model", ofType: "tflite") let options = ObjectDetectorOptions() options.baseOptions.modelAssetPath = modelPath options.runningMode = .video options.maxResults = 5 let objectDetector = try ObjectDetector(options: options)
livestream
import MediaPipeTasksVision // Class that conforms to the `ObjectDetectorLiveStreamDelegate` protocol and // implements the method that the object detector calls once it // finishes performing detection on each input frame. class ObjectDetectorResultProcessor: NSObject, ObjectDetectorLiveStreamDelegate { func objectDetector( _ objectDetector: ObjectDetector, didFinishDetection objectDetectionResult: ObjectDetectorResult?, timestampInMilliseconds: Int, error: Error?) { // Process the detection result or errors here. } } let modelPath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "model", ofType: "tflite") let options = ObjectDetectorOptions() options.baseOptions.modelAssetPath = modelPath options.runningMode = .liveStream options.maxResults = 5 // Assign an object of the class to the `objectDetectorLiveStreamDelegate` // property. let processor = ObjectDetectorResultProcessor() options.objectDetectorLiveStreamDelegate = processor let objectDetector = try ObjectDetector(options: options)
Objective-C
Image
@import MediaPipeTasksVision; NSString *modelPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"model" ofType:@"tflite"]; MPPObjectDetectorOptions *options = [[MPPObjectDetectorOptions alloc] init]; options.baseOptions.modelAssetPath = modelPath; options.runningMode = MPPRunningModeImage; options.maxResults = 5; MPPObjectDetector *objectDetector = [[MPPObjectDetector alloc] initWithOptions:options error:nil];
Video
@import MediaPipeTasksVision; NSString *modelPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"model" ofType:@"tflite"]; MPPObjectDetectorOptions *options = [[MPPObjectDetectorOptions alloc] init]; options.baseOptions.modelAssetPath = modelPath; options.runningMode = MPPRunningModeVideo; options.maxResults = 5; MPPObjectDetector *objectDetector = [[MPPObjectDetector alloc] initWithOptions:options error:nil];
livestream
@import MediaPipeTasksVision; // Class that conforms to the `ObjectDetectorLiveStreamDelegate` protocol and // implements the method that the object detector calls once it // finishes performing detection on each input frame. @interface APPObjectDetectorResultProcessor : NSObject@end @implementation MPPObjectDetectorResultProcessor - (void)objectDetector:(MPPObjectDetector *)objectDetector didFinishDetectionWithResult:(MPPObjectDetectorResult *)ObjectDetectorResult timestampInMilliseconds:(NSInteger)timestampInMilliseconds error:(NSError *)error { // Process the detection result or errors here. } @end NSString *modelPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"model" ofType:@"tflite"]; MPPObjectDetectorOptions *options = [[MPPObjectDetectorOptions alloc] init]; options.baseOptions.modelAssetPath = modelPath; options.runningMode = MPPRunningModeLiveStream; options.maxResults = 5; // Assign an object of the class to the `objectDetectorLiveStreamDelegate` // property. APPObjectDetectorResultProcessor *processor = [APPObjectDetectorResultProcessor new]; options.objectDetectorLiveStreamDelegate = processor; MPPObjectDetector *objectDetector = [[MPPObjectDetector alloc] initWithOptions:options error:nil];
Configuration options
This task has the following configuration options for iOS apps:
| Option Name | Description | Value Range | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
runningMode |
Sets the running mode for the task. There are three
modes: IMAGE: The mode for single image inputs. VIDEO: The mode for decoded frames of a video. LIVE_STREAM: The mode for a livestream of input data, such as from a camera. In this mode, resultListener must be called to set up a listener to receive results asynchronously. |
{RunningMode.image, RunningMode.video, RunningMode.liveStream} |
RunningMode.image |
displayNamesLocales |
Sets the language of labels to use for display names provided in the
metadata of the task's model, if available. Default is en for
English. You can add localized labels to the metadata of a custom model
using the TensorFlow Lite Metadata Writer API
|
Locale code | en |
maxResults |
Sets the optional maximum number of top-scored detection results to return. | Any positive numbers | -1 (all results are returned) |
scoreThreshold |
Sets the prediction score threshold that overrides the one provided in the model metadata (if any). Results below this value are rejected. | Any float | Not set |
categoryAllowlist |
Sets the optional list of allowed category names. If non-empty,
detection results whose category name is not in this set will be
filtered out. Duplicate or unknown category names are ignored.
This option is mutually exclusive with categoryDenylist and using
both results in an error. |
Any strings | Not set |
categoryDenylist |
Sets the optional list of category names that are not allowed. If
non-empty, detection results whose category name is in this set will be filtered
out. Duplicate or unknown category names are ignored. This option is mutually
exclusive with categoryAllowlist and using both results in an error. |
Any strings | Not set |
Livestream configuration
When the running mode is set to livestream, the Object Detector requires the
additional objectDetectorLiveStreamDelegate configuration option, which
enables the detector to deliver detection results asynchronously. The delegate
implements the
objectDetector(_objectDetector:didFinishDetection:timestampInMilliseconds:error:)
method, which the Object Detector calls after processing the detection result for
each frame.
| Option name | Description | Value Range | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
objectDetectorLiveStreamDelegate |
Enables Object Detector to receive detection results asynchronously in
livestream mode. The class whose instance is set to this property must
implement the
objectDetector(_:didFinishDetection:timestampInMilliseconds:error:)
method. |
Not applicable | Not set |
Prepare data
You need to convert the input image or frame to an MPImage object before
passing it to the Object Detector. MPImage supports different types of iOS image
formats, and can use them in any running mode for inference. For more
information about MPImage, refer to the
MPImage API.
Choose an iOS image format based on your use case and the running mode your
application requires.MPImage accepts the UIImage, CVPixelBuffer, and
CMSampleBuffer iOS image formats.
UIImage
The UIImage format is well-suited for the following running modes:
Images: images from an app bundle, user gallery, or file system formatted as
UIImageimages can be converted to anMPImageobject.Videos: use AVAssetImageGenerator to extract video frames to the CGImage format, then convert them to
UIImageimages.
Swift
// Load an image on the user's device as an iOS `UIImage` object. // Convert the `UIImage` object to a MediaPipe's Image object having the default // orientation `UIImage.Orientation.up`. let image = try MPImage(uiImage: image)
Objective-C
// Load an image on the user's device as an iOS `UIImage` object. // Convert the `UIImage` object to a MediaPipe's Image object having the default // orientation `UIImageOrientationUp`. MPImage *image = [[MPPImage alloc] initWithUIImage:image error:nil];
The example initializes an MPImage with the default
UIImage.Orientation.Up
orientation. You can initialize an MPImage with any of the supported
UIImage.Orientation
values. Object Detector does not support mirrored orientations like .upMirrored,
.downMirrored, .leftMirrored, .rightMirrored.
For more information about UIImage, refer to the UIImage Apple Developer
Documentation.
CVPixelBuffer
The CVPixelBuffer format is well-suited for applications that generate frames
and use the iOS CoreImage
framework for processing.
The CVPixelBuffer format is well-suited for the following running modes:
Images: apps that generate
CVPixelBufferimages after some processing using iOS'sCoreImageframework can be sent to the Object Detector in the image running mode.Videos: video frames can be converted to the
CVPixelBufferformat for processing, and then sent to the Object Detector in video mode.livestream: apps using an iOS camera to generate frames may be converted into the
CVPixelBufferformat for processing before being sent to the Object Detector in livestream mode.
Swift
// Obtain a CVPixelBuffer. // Convert the `CVPixelBuffer` object to a MediaPipe's Image object having the default // orientation `UIImage.Orientation.up`. let image = try MPImage(pixelBuffer: pixelBuffer)
Objective-C
// Obtain a CVPixelBuffer. // Convert the `CVPixelBuffer` object to a MediaPipe's Image object having the // default orientation `UIImageOrientationUp`. MPImage *image = [[MPPImage alloc] initWithUIImage:image error:nil];
For more information about CVPixelBuffer, refer to the CVPixelBuffer Apple
Developer
Documentation.
CMSampleBuffer
The CMSampleBuffer format stores media samples of a uniform media type, and is
well-suited for the livestream running mode. Live frames from iOS cameras are
asynchronously delivered in the CMSampleBuffer format by iOS
AVCaptureVideoDataOutput.
Swift
// Obtain a CMSampleBuffer. // Convert the `CMSampleBuffer` object to a MediaPipe's Image object having the default // orientation `UIImage.Orientation.up`. let image = try MPImage(sampleBuffer: sampleBuffer)
Objective-C
// Obtain a `CMSampleBuffer`. // Convert the `CMSampleBuffer` object to a MediaPipe's Image object having the // default orientation `UIImageOrientationUp`. MPImage *image = [[MPPImage alloc] initWithSampleBuffer:sampleBuffer error:nil];
For more information about CMSampleBuffer, refer to the CMSampleBuffer Apple
Developer
Documentation.
Run the task
To run the Object Detector, use the detect() method specific to the assigned
running mode:
- Still image:
detect(image:) - Video:
detect(videoFrame:timestampInMilliseconds:) - livestream:
detectAsync(image:)
The following code samples show basic examples of how to run Object Detector in these different running modes:
Swift
Image
let objectDetector.detect(image:image)
Video
let objectDetector.detect(videoFrame:image)
livestream
let objectDetector.detectAsync(image:image)
Objective-C
Image
MPPObjectDetectorResult *result = [objectDetector detectInImage:image error:nil];
Video
MPPObjectDetectorResult *result = [objectDetector detectInVideoFrame:image timestampInMilliseconds:timestamp error:nil];
livestream
BOOL success = [objectDetector detectAsyncInImage:image timestampInMilliseconds:timestamp error:nil];
The Object Detector code example shows the implementations of each of these modes
in more detail detect(image:), detect(videoFrame:), and
detectAsync(image:). The example code allows the user to switch between
processing modes which may not be required for your use case.
Note the following:
When running in video mode or livestream mode, you must also provide the timestamp of the input frame to the Object Detector task.
When running in image or video mode, the Object Detector task blocks the current thread until it finishes processing the input image or frame. To avoid blocking the current thread, execute the processing in a background thread using iOS Dispatch or NSOperation frameworks.
When running in livestream mode, the Object Detector task returns immediately and doesn't block the current thread. It invokes the
objectDetector(_objectDetector:didFinishDetection:timestampInMilliseconds:error:)method with the detection result after processing each input frame. The Object Detector invokes this method asynchronously on a dedicated serial dispatch queue. For displaying results on the user interface, dispatch results to the main queue after processing the results. If thedetectAsyncfunction is called when the Object Detector task is busy processing another frame, the Object Detector ignores the new input frame.
Handle and display results
Upon running inference, the Object Detector task returns an ObjectDetectorResult
object which describes the objects that it has found in the input image.
The following shows an example of the output data from this task:
ObjectDetectorResult:
Detection #0:
Box: (x: 355, y: 133, w: 190, h: 206)
Categories:
index : 17
score : 0.73828
class name : dog
Detection #1:
Box: (x: 103, y: 15, w: 138, h: 369)
Categories:
index : 17
score : 0.73047
class name : dog
The following image shows a visualization of the task output:
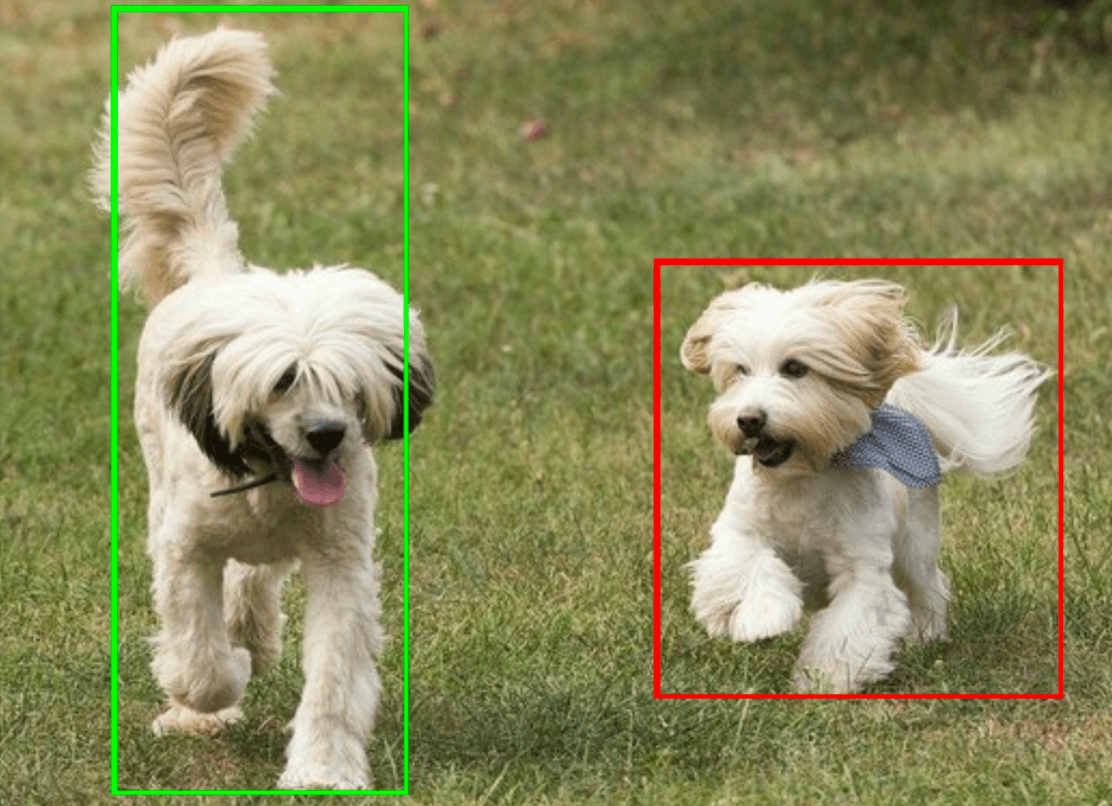
The Object Detector example code demonstrates how to display the detection results returned from the task, see the code example for details.
